EZH2
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) EC 2.1.1.43 is a lysine methyltransferase and is the catalytic subunit of the PRC2 complex responsible for the methylation of histone H3. Overexpression of EZH2 has been linked multiple types of cancer.
EZH2 Inhibitors |
|
|---|---|
| Cat. No. | 产品名称/活性 |
| 4703 | 3-Deazaneplanocin A hydrochloride |
| EZH2 histone methyltransferase inhibitor | |
| 6790 | GSK 126 |
| Very high affinity and selective EZH2 inhibitor | |
| 6128 | GSK 343 |
| Potent and selective SAM-competitive EZH2 inhibitor | |
| 6153 | JQEZ5 |
| Potent and selective SAM-competitive EZH2 inhibitor | |
| 6169 | PF 06726304 acetate |
| Highly potent and SAM-competitive EZH2 inhibitor | |
| 8093 | Tazemetostat |
| Potent and selective EZH2 inhibitor | |
| 4904 | UNC 1999 |
| Potent and selective EZH2/EZH1 inhibitor | |
Degraders |
|
| Cat. No. | 产品名称/活性 |
| 7816 | UNC 6852 |
| EZH2 Degrader (PROTAC®) | |
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) EC 2.1.1.43 is a lysine methyltransferase that catalyses the transfer of methyl groups from S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) to histone H3 at lysine 27. This facilitates the formation of heterochromatin and regulates gene expression.
EZH2 is the catalytic subunit of the polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) complex which regulates cell fate. Methylation of H3 by the complex leads to silencing of target genes involved in cell cycle regulation, cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cancer progression. In human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), EZH2 plays roles in the maintenance of pluripotency, self-renewal, proliferation and differentiation.
Genetic, transcriptional and post-transcription dysregulation of EZH2 are frequently identified in cancers. Mutations and overexpression of EZH2 have been linked to breast, prostate and bladder cancer, as well as melanomas. Inhibition of EZH2 represents a potential therapeutic avenue as EZH2 inhibits tumor growth suppression genes.
External sources of pharmacological information for EZH2 :
Literature for EZH2
Tocris offers the following scientific literature for EZH2 to showcase our products. We invite you to request* your copy today!
*Please note that Tocris will only send literature to established scientific business / institute addresses.
Epigenetics Scientific Review
Written by Susanne Müller-Knapp and Peter J. Brown, this review gives an overview of the development of chemical probes for epigenetic targets, as well as the impact of these tool compounds being made available to the scientific community. In addition, their biological effects are also discussed. Epigenetic compounds available from Tocris are listed.
Stem Cells Scientific Review
Written by Kirsty E. Clarke, Victoria B. Christie, Andy Whiting and Stefan A. Przyborski, this review provides an overview of the use of small molecules in the control of stem cell growth and differentiation. Key signaling pathways are highlighted, and the regulation of ES cell self-renewal and somatic cell reprogramming is discussed. Compounds available from Tocris are listed.
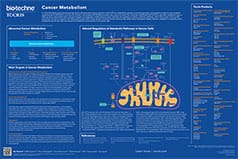
Cancer Metabolism Poster
This poster summarizes the main metabolic pathways in cancer cells and highlights potential targets for cancer therapeutics. Genetic changes and epigenetic modifications in cancer cells alter the regulation of cellular metabolic pathways providing potential cancer therapeutic targets.
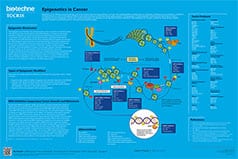
Epigenetics in Cancer Poster
This poster summarizes the main epigenetic targets in cancer. The dysregulation of epigenetic modifications has been shown to result in oncogenesis and cancer progression. Unlike genetic mutations, epigenetic alterations are considered to be reversible and thus make promising therapeutic targets.