Glucose Transporters
Glucose transporters enable the movement of glucose, a hydrophilic molecule, across the cell membrane. Glucose is an essential source of energy for mammalian cells, and is also used as a substrate in protein and lipid synthesis.
To view Bio-Techne's complete solutions for lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, and energy balance, please visit our metabolism page on bio-techne.com
Glucose Transporter Inhibitors |
|
|---|---|
| Cat. No. | 产品名称/活性 |
| 6199 | BAY 876 |
| Potent and selective GLUT1 inhibitor | |
| 4484 | STF 31 |
| GLUT1 inhibitor; also NAMPT inhibitor | |
| 6143 | WZB 117 |
| GLUT inhibitor | |
Other |
|
| Cat. No. | 产品名称/活性 |
| 6065 | 2-NBDG |
| Fluorescent glucose uptake indicator | |
| 7447 | SCOTfluor glucose probe 510 |
| Fluorescent glucose probe | |
Glucose is an essential source of energy for mammalian cells, and is also used as a substrate in protein and lipid synthesis. Given its hydrophilic nature, glucose must be transported into the cell by dedicated transporters; these are encoded by genes known collectively as the facilitative glucose transporter gene family (GLUT). There are 13 known members of the GLUT family.
Glucose transporters maintain a ready supply of glucose for the cell's metabolic activity. During growth and division, the energy demands of a cell are increased; it needs glucose to generate ATP and biomass. Cancer cells, which proliferate at a greater rate, thus require more energy than a normal cell. Aerobic glycolysis - often observed in tumor cells, and also known as the Warburg effect - relies on a high rate of glucose uptake, since the generation of ATP by this process is far less efficient than oxidative phosphorylation. Glucose transporters, in particular GLUT1, have therefore become a target of interest in cancer research, as have glycolytic inhibitors.
External sources of pharmacological information for Glucose Transporters :
Literature for Glucose Transporters
Tocris offers the following scientific literature for Glucose Transporters to showcase our products. We invite you to request* your copy today!
*Please note that Tocris will only send literature to established scientific business / institute addresses.
Cancer Metabolism Research Product Guide
This product guide reviews some of the main areas in cancer metabolism research and lists around 150 products that can be used to investigate metabolic pathways in cancer including:
- Glycolysis
- Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
- Lipidogenesis
- 1C Metabolism and Nucleic Acid Synthesis
- Drivers of Metabolic Reprogramming
- pH and Redox Balance
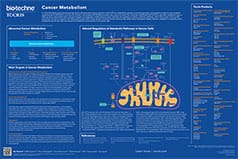
Cancer Metabolism Poster
This poster summarizes the main metabolic pathways in cancer cells and highlights potential targets for cancer therapeutics. Genetic changes and epigenetic modifications in cancer cells alter the regulation of cellular metabolic pathways providing potential cancer therapeutic targets.
Glucose Transporter Gene Data
| Gene | Species | Gene Symbol | Gene Accession No. | Protein Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 1
(GLUT1) |
Human | SLC2A1 | NM_006516 | P11166 |
| Mouse | Slc2a1 | NM_011400 | P17809 | |
| Rat | Slc2a1 | NM_138827 | P11167 | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 2
(GLUT2) |
Human | SLC2A2 | NM_000340 | P11168 |
| Mouse | Slc2a2 | NM_031197 | P14246 | |
| Rat | Slc2a2 | NM_012879 | P12336 | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 3
(GLUT3) |
Human | SLC2A3 | NM_006931 | P11169 |
| Mouse | Slc2a3 | NM_011401 | P32037 | |
| Rat | Slc2a3 | NM_017102 | Q6P506 | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 4
(GLUT4) |
Human | SLC2A4 | NM_001042 | P14672 |
| Mouse | Slc2a4 | NM_009204 | P14142 | |
| Rat | Slc2a4 | NM_012751 | P19357 | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 5
(GLUT5) |
Human | SLC2A5 | NM_003039 | P22732 |
| Mouse | Slc2a5 | NM_019741 | Q9WV38 | |
| Rat | Slc2a5 | NM_031741 | P43427 | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 6
(GLUT6) |
Human | SCL2A6 | NM_017585 | Q9UGQ3 |
| Mouse | Slc2a6 | NM_172659 | Q3UDF0 | |
| Rat | Slc2a6 | NM_001106562 | EDL93446 | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 7
(GLUT7) |
Human | SCL2A7 | NM_207420 | Q6PXP3 |
| Mouse | Slc2a7 | NM_001085529 | B1ARZ3 | |
| Rat | Slc2a7 | NM_001101020 | A4ZYQ5 | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 8
(GLUT8) |
Human | SLC2A8 | NM_014580 | Q9NY64 |
| Mouse | Slc2a8 | NM_019488 | Q9IJF3 | |
| Rat | Slc2a8 | NM_053494 | Q9JJZ1 | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 9
(GLUT9) |
Human | SCL2A9 | NM_001001290 | Q9NRM0 |
| Mouse | Slc2a9 | NM_001102414 | Q3T9X0 | |
| Rat | - | - | - | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 10
(GLUT10) |
Human | SLC2A10 | NM_030777 | O95528 |
| Mouse | Slc2a10 | NM_130451 | Q8VHD6 | |
| Rat | Slc2a10 | NM_001108963 | EDL96452 | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 11
(GLUT11) |
Human | SLC2A11 | NM_030807 | Q9BYW1 |
| Mouse | - | - | - | |
| Rat | - | - | - | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 12
(GLUT12) |
Human | SLC2A12 | NM_145176 | Q8TD20 |
| Mouse | Slc2a12 | NM_178934 | Q8BFW9 | |
| Rat | Slc2a12 | NM_001107451 | EDL87731 | |
|
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 13
(HMIT) |
Human | SLC2A13 | NM_052885 | Q96QE2 |
| Mouse | Slc2a13 | NM_001033633 | Q3UHK1 | |
| Rat | Slc2a13 | NM_133611 | Q921A2 |